Importance of vaccines from India and how they work
For more than 70 years’ vaccines are saving billions of people and battled life threatening illnesses. Even though some diseases like whooping cough, measles and mumps are still prevalent, immunity doses in childhood save them. Currently, India exports various vaccines to resistinfections. Manufacturers make branded and generic serums and injections that are widely effective in western countries.
Lotus International, based in Mumbai is an active exporter of vaccines for the world market. Our formulations reach other continents and follow international protocols to make Havrix, Havpur, Impovax Polio and InfanrixBoostrix, Cervarix, BCG ONCO BP (Intravesical), Fluarix and Gardasil.

This post explains about immunization the body’s system to attack infections, germs and viruses. It also highlights how vaccines reduce the risk of infections and keeps us healthy.
Working ofa typical vaccine works after being injected into the body
When introduced into the body, a shot will imitate the infection. The primary aim is to produce antibodies and T-lymphocytes. Due to imitation, some minor symptoms like fever are experienced by the patient on receiving the injection. This indicates the body is building its immunity system and the dose is working. As the imitation of infection fades only the memory of T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytesstay back. The cells are now equipped to fight future infections. The body takes some time to produce the T-lymphocytes after the booster dose is given thereby offering protection.
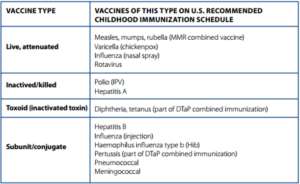
Types of vaccines administered
For the last several decades’ scientists are developing potent vaccines. Trials are conducted based on information of the disease for developing better compositions. New generation of viruses and bacteria loads reveal viral attacks are common. Vaccines are being developed to counter germs that infect the body’s cells.
In India, manufacturing units are equipped to conduct clinical tests as demands from the markets arise.
The main types are:
- Live tempered vaccines– for virus and bacteria. They are used for mumps and measles.
- Inactive vaccines-The germs are killed when the injection is made. The polio vaccine is the best example of it. They tend to produce a different immune response compared to tempered vaccines.
- Toxoid Vaccines-Toxins produced by the body can be poisonous. The bacterial toxins are weakened when the injection or serum is being made. They support the immune system to fight the poison in the body.
- Subunit vaccines– These contain only the essential antigen required to fight the disease, virus or bacteria. They cause fewer side effects. In the case of whooping cough, it works. The DTaP vaccine is common in such cases.
- Conjugate vaccines-Some bacteria have an outer coating called polysaccharides. A small child’s immune system is unable to recognize the problem it creates and responds to the attack. The conjugate vaccines play a vital role in saving the child’s life. The Haemophilus influenza is an example of this type of vaccine.
Lotus International takes into account practical considerations where the inoculations packages are exported like: The environmental conditions under which they are produced, the temperatures required for packaging and solutions for handling consignment during delivery are vital. As risks of infections rise all over the globe, it is vital to consider how serums reach end-consumers.